A Network Map for USDA’s Climate-Smart Commodities Program
7 September 2023By: Todd Barker and Katrina Sarandrea
The role of the agriculture sector in climate mitigation and adaptation is a growing focus of domestic and international climate efforts. As a significant source of greenhouse gas emissions, agriculture’s mitigation potential lies in adopting sustainable practices that sequester carbon, reduce emissions, enhance overall resource efficiency, and provide co-benefit (e.g., improved water quality).
The Biden-Harris Administration is investing a historic $3 billion in 141 projects to support the production and marketing of climate-smart commodities, which USDA defines as any agricultural commodity that is produced using practices that reduce gas emissions or sequester carbon. The program, known as the USDA Partnerships for Climate-Smart Commodities, helps farmers address the effects of climate change on our global food systems by:
- Providing technical and financial assistance to producers to implement climate-smart production practices on a voluntary basis on working lands;
- Piloting innovative and cost-effective methods for quantification, monitoring, reporting and verification of greenhouse gas benefits; and,
- Developing markets and promoting the resulting climate-smart commodities.
This historic program is investing in 141 selected projects, which each have a network of supporting partners, a list of target conservation practices, and varying geographic scope. The size and importance of this investment caused many agriculture and conservation-focused organizations to ask questions including:
Where is the Climate-Smart Commodities program directing its investment?
What climate-smart practices are being emphasized, and for what production systems?
How can the private sector predict the increased demand for inputs and services and increase supply to enable the implementation of these projects?
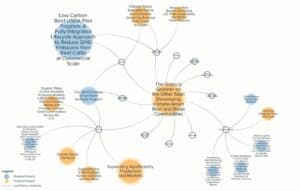
Meridian Institute applied its long-standing experience in landscape and stakeholder analysis to help answer these questions through developing the Climate-Smart Commodities Network Map. The purpose of the map is to help the public and private sectors better understand how these historic federal investments are being implemented and impacting communities. The network map creates a visual representation of the relationships and connections between individual projects, partner organizations, and other aspects of the program.
We believe this approach will help foster opportunities for collaboration and innovation among those involved in the program.
- Climate-Smart Commodity Program Grantees benefit from discovering projects with similar objectives or focus areas they can connect with, learn from, and collaborate.
- Agricultural Producers benefit from learning which climate-smart projects are relevant to their areas of interest and connecting to projects they might sign up with.
- Policymakers benefit from exploring where and how USDA project funding is being directed and the potential impacts of the program overall.
- Philanthropies benefit from discovering which organizations are advancing projects aligned with their interests and how they might make complimentary investments to ensure the success of the program.
- Companies benefit from learning where they can anticipate an increase in demand for inputs and associated services that will be generated through the projects.
At Meridian, we recognize that network and systems mapping is critical to building understanding, informing decisions, and driving action to address critical global challenges like climate change.
To learn more about our systems work and how we might support your organization’s strategic goals, contact us at contact@merid.org.
Explore the Map
For more information on the Climate-Smart Commodities Network Map, go to climatesmart.merid.org. The map is hosted on Kumu, a network visualization platform. To explore it, you can click here. Note you will be asked to complete a brief form before accessing the map.